New species of Drown dinosaurs Discovered: Taleta Taleta

Paleontologists have identified a new genus and species of small haadrosaurid dinosaurs of the lambosaurine of two fossilized jaws found in Morocco.
The reconstruction of an artist of Take taida. Image credit: Connor Ashbridge.
Take taida lived in what is now Morocco at the end of the Cretaceous era, about 66 million years ago.
“The Cretaceous period experienced the final stages of the rupture of the Supercontinent pangea and the high eustatic sea level,” said the paleontologist of the University of Bath Nicholas Longrich and his colleagues from Spain, France and Morocco.
“Consequently, the earth’s masses of the earth have been fragmented to form a series of isolated island continents, leading to the evolution of fauna of distinct dinosaurs in different parts of the world.”
“Asia and North America were dominated by Hadrosaurides and Ceratopsian ornithisian, and tyrannosaurid theropods have reigned as predators.”
“In the southern hemisphere, Titanosaurian sauropods were dominant herbivores and abélisaurids dominated as predators.”
“Although isolation has played an important role in the conduct of biogeographic models, it is increasingly clear that dispersion has played an important role, especially towards the end of the Cretaceous.”
The two associated jaws of Take taida have been found in the highest Maastrichtians in Morocco.
“The phosphates of the Oulad Abdoun basin, located in the center of Morocco, consist of a series of phosphatic sands, marls and limestones deposited in a shallow marine environment at a time when the North Atlantic has extended to the land to cover a large part of Morocco,” said paleontologists.
“Phosphates extend over the Maastrichtian (72 to 66 million years ago) in the start of the Eocene (56 million years ago).”
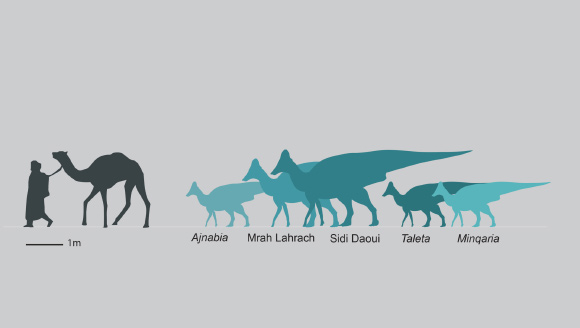
The lambosaurine dinosaurs were diverse in Morocco, with at least three coexisting species. Image credit: Longrich and al., Two: 10.1016 / J.GR.2025.05.006.
Take taida Belongs to the Lambeosaurine Arenysaurini tribe and its discovery bears the total number of arenysaurin species known to the phosphates from Morocco to three.
“The discovery of the first Hadrosauride of Maastrichtian phosphates in Morocco, Ajnabia Ulyssehas shown that, despite their insulation by the oceans, the Hadrosaurides have managed to disperse in Africa in the last Cretaceous, “said the researchers.
“Close affinities of Stranger With the Arenysaurini, otherwise known only by Armorica, suggest that the dispersed clade of southern Europe. »»
“More recently, a second Arenysaurin, Minqaria Bata Batwas reported in the same layers. »»
“”Minqaria Bata Bat differs considerably in the shape of jaws and teeth Strangersuggesting a specialization for separate niches. »»
“Recently, the upper jaws associated with a small duck billiard dinosaur were discovered in phosphates.”
“Remarkably, this specimen cannot be referred either Stranger Or Minqaria. Instead, it represents a third genus and species. »»
“The striking variation in the morphology of the jaw and teeth observed in African areas suggests an adaptive radiation focused on dispersion, the labbeosaurins quickly diversifying to occupy new niches after the dispersion of Europe in North Africa,” they concluded.
“African influence has coincided with the decline of lambosaurine in North America, emphasizing the highly regional nature of the evolution of dinosaurs.”
The team’s article was published in the newspaper Gondwana search.
_____
Nicholas R. Longrich and al. A new Hadrosauride dinosauride from the end of the Maastrichtians phosphates of Morocco provides evidence of African lambosaurins influence. Gondwana searchpublished online on May 28, 2025; DOI: 10.1016 / J.GR.2025.05.006




