Know the differences between meteors, weather, meteorites, comets and asteroids

Astronomy is riddled with a complex jargon that many of us will probably never need to understand. However, you are more likely to read and hear about meteors, weather, meteorites, comets and online asteroids and in the news, so here is a break in what they are.
Meteor
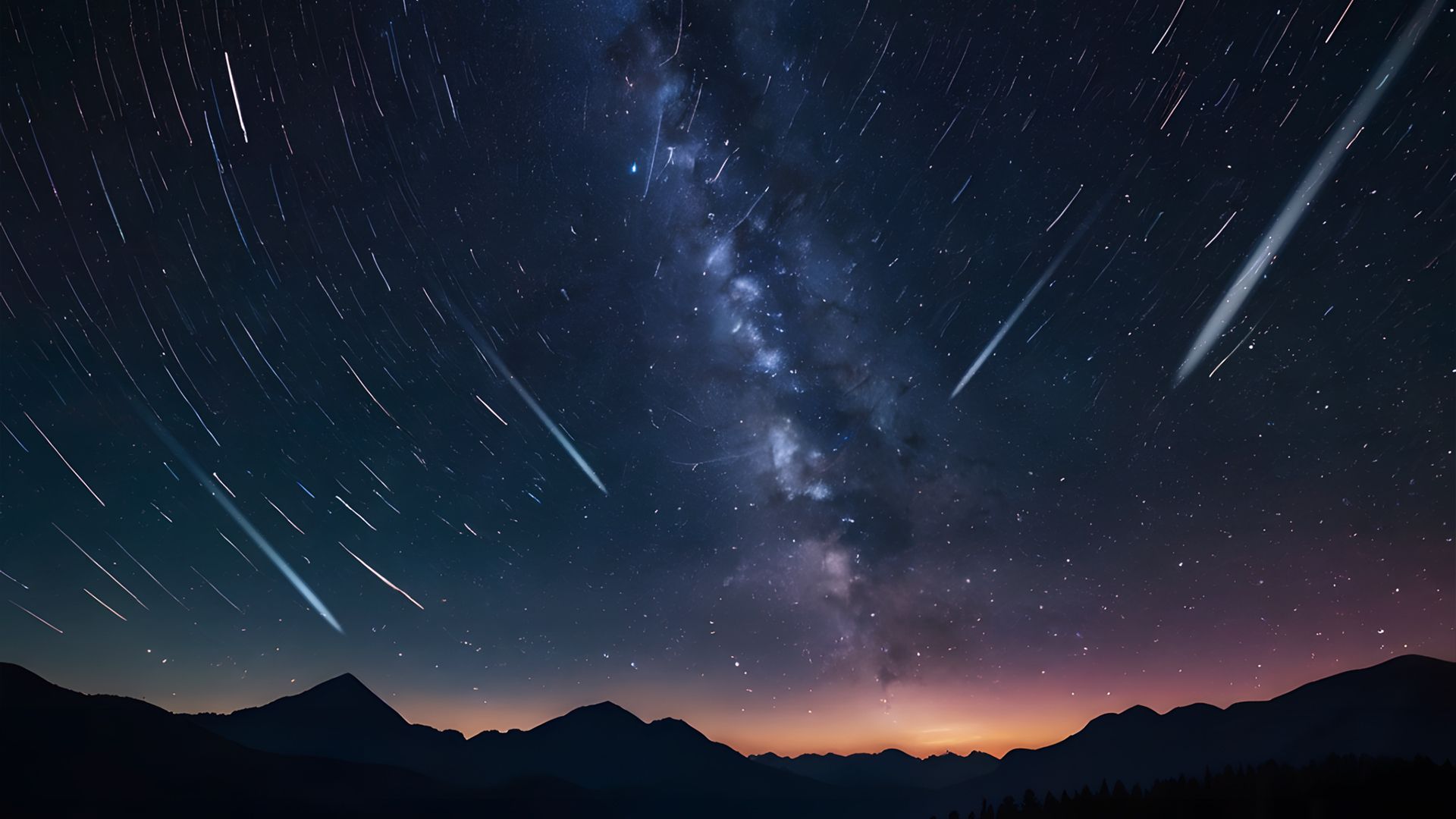
Meteors occur when a meteoroid particle or space enters the earth’s atmosphere at very high speeds (up to 46 miles per second!), Causing violent air compression, high temperatures and a sequence of light.
The sporadic meteors are caused when the wandering weather collide with our atmosphere, while meteor showers are the result of the Earth path crossing a flow of debris. Meteor showers can be easily observed in the naked eye in the right conditions, and as the earth’s orbit is relatively consistent, we can predict when they should occur each year.

Related
I looked at many meteor showers – here’s how you can also
There is more in our sky than constellations and planets.
Meteor showers vary in their intensity. The geminid meteor shower, which culminates at the end of the second week of December each year, can produce up to 100 meteors per hour, while the meteor shower Lyrid, which culminates around the end of April, usually offers up to 15 of the hour.
Meteoroid
A meteoroid is a small piece of spatial debris from larger bodies in space, such as comets, asteroids, other planets and the moon. These pieces of debris are only called meteoroids when they travel in space – they become meteors when they burn in our atmosphere or meteorites if they cross and strike the surface of the earth.
Various celestial events can cause a meteoroid shape, such as a comet which stands out from the sun, collisions between asteroids and planetary ejections. Consequently, their composition can vary: some meteoroids are rocky, others metallic and a combination of the two.
Météoroids can also vary in size, ranging as small as a grain of dust as large as a meter in diameter. Since there is an infinite number of meteoroids floating in the cosmos, they are not names.
Meteorite
A meteorite is a meteoroid that strikes the surface of the earth, having survived the rupture through the earth’s atmosphere. If he had not survived this trip, separating instead into the earth’s atmosphere, he would have become a meteor.

Related
Meteorites are much more amazing than you think
These are not really filming stars; These are just cosmic debris, accelerating in a hell.
So what determines if a meteoroid becomes a meteor or a meteorite? In fact, a combination of factors determines its fate, including its composition, size, density, aerodynamic efficiency and its entrance angle. The larger iron meteors tend to be robust enough to resist intense heat and the pressure exerted on them during entry, allowing them to become meteorites when they break.
However, their chance of survival also depends on whether they adopt a conical form during their travels, and if they can avoid collision with our atmosphere at an overly steep angle.
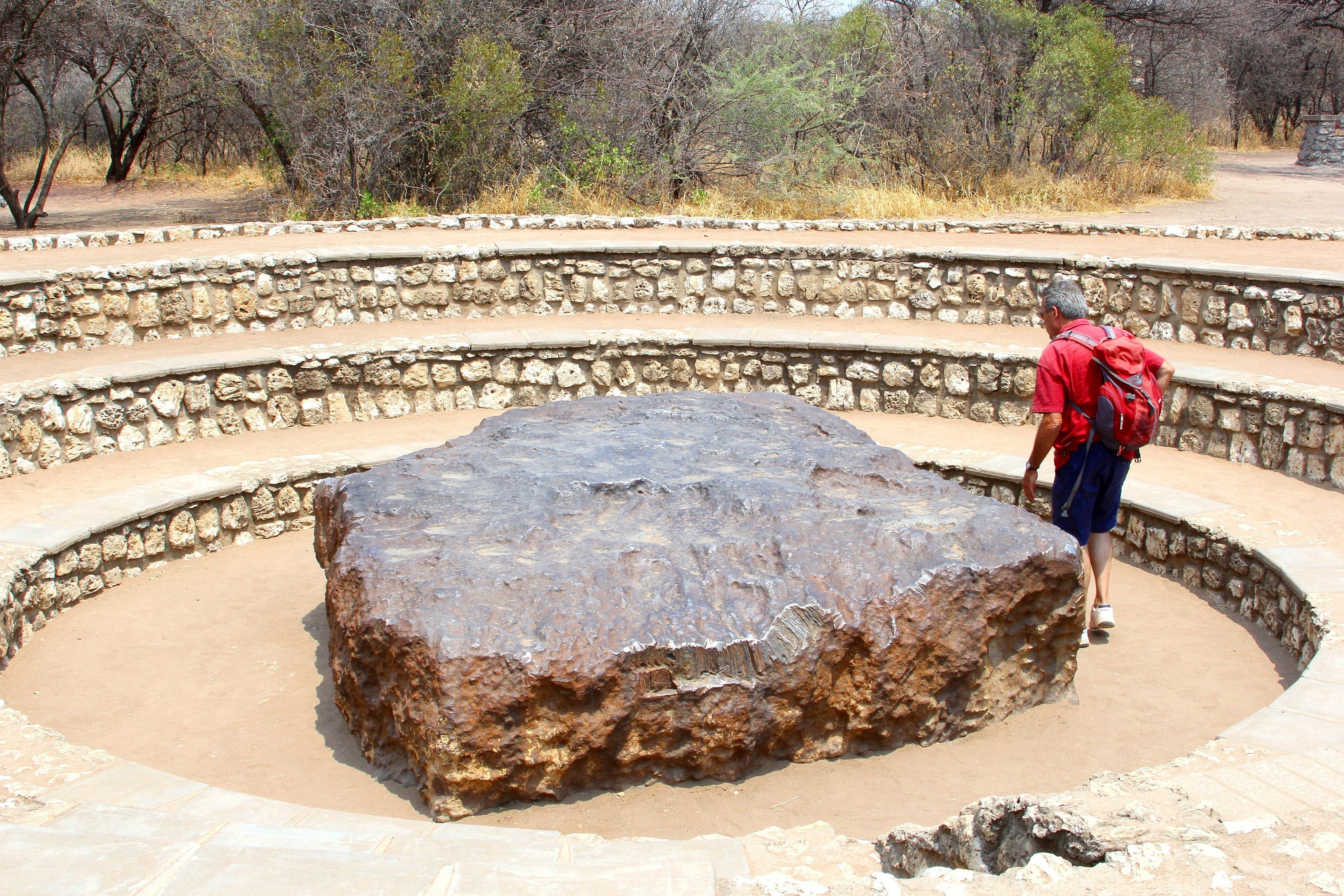
The meteorite Hoba, discovered on a farm in Namibia in 1920 but which would have crossed the atmosphere about 80,000 years ago, is the largest intact meteorite in the world. It measures approximately 2.7 meters in diameter 2.7 meters deep 0.9 meters high, should have a mass of approximately 642 tonnes and is made up of around 84% iron, 16% nickel and cobalt traces.
Did you know? In 1920, the mass of Hoba was estimated at around 667 tonnes. However, erosion, scientific sampling and vandalism have reduced its mass over time.
Comet
Compets are celestial bodies of ice, dust and rock – to be a residual material of the formation of the solar system – which orbit the sun in the Kuiper belt and the Oort cloud. When they pass through the inner solar system, solar heating leads them to adopt a coma (a shiny head) and dust and gas tails (caused by the solar wind and radiation). According to NASA, when it is frozen, comets can be as large as a small town.
While comets pass the earth quite frequently, seeing a brilliant event is a rare event. A recent notable exception was c / 2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan -Atlas), which surprised astronomers – amateur and professional – with its slight tail and its apparently stationary position in the sky for about two weeks.
To see a lower comet, you will most likely have to travel a telescope, such as the Celestron 114LCM computerized telescope.
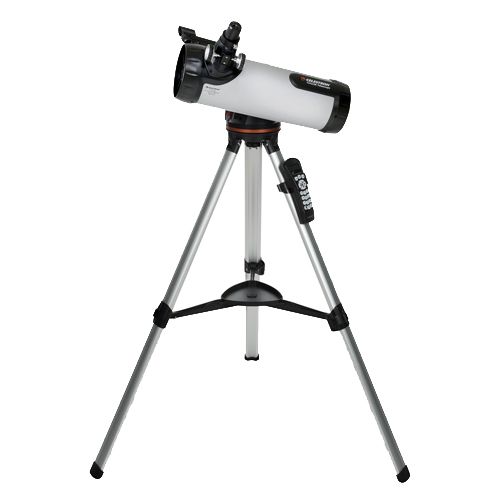

Celestron 114LCM computerized telescope
With an opening of 4.49 inches (114 mm) and a focal length of 39 inches (1000 mm), the Celestron 114LCM provides a maximum magnification of 269x – a lot to see the planets, the moon and some deep sky objects. The support is computerized, which facilitates the research and monitoring of objects of interest. Once you calibrate it, you are ready!
Many comets have two names: their code name of the international astronomical union (IAU) (like C / 2023 A3), and their name of discoverer (like Tsuchinshan-Atlas).
In “C / 2023 A3”, “C” means that he is officially recognized as a comet, “2023” indicates that the year it was discovered for the first time, while “A3” means that it was the third comet to be discovered in the first half of the same year. “Tsuchinshan-Atlas” means that the comet was seen for the first time at the Chinese Observatory of Tsuchinshan before being officially confirmed shortly by the latest asteroid alert system (Atlas).
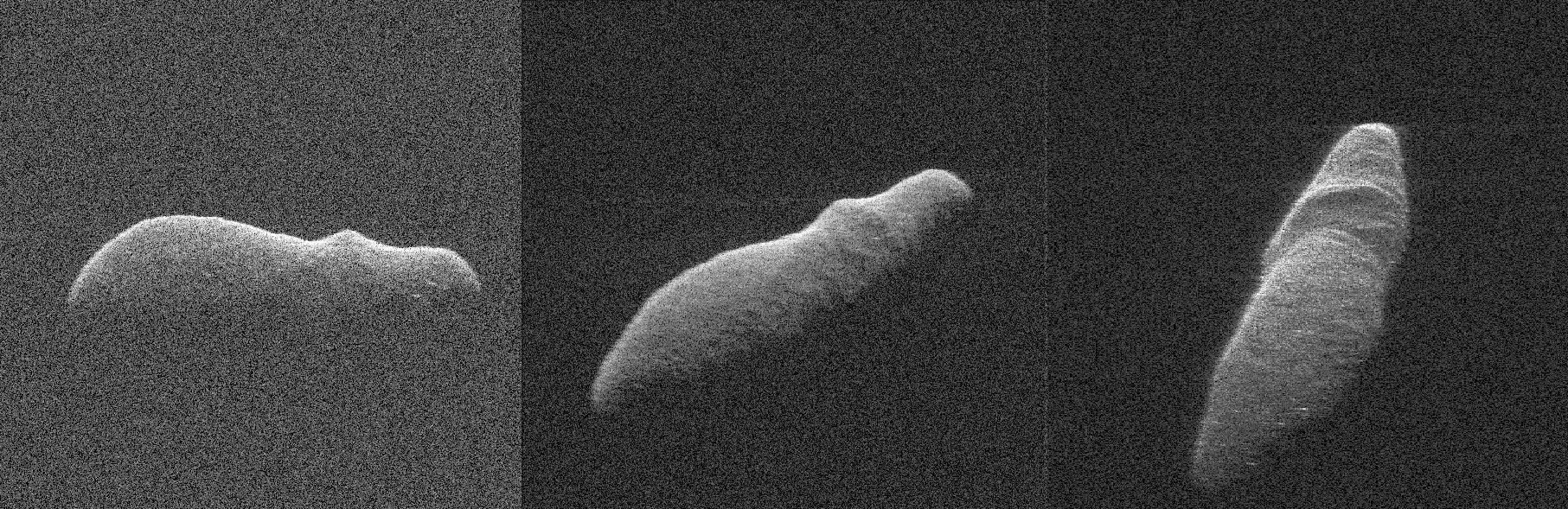
Asteroid
People often confuse weather and asteroids, probably because they are made of similar materials (rock and metal), and they both orbit the sun. However, although the weather is generally up to a meter in diameter, asteroids are generally a few meters to hundreds of kilometers.
That said, when an asteroid breaks, its leftovers can be classified as meteoroids.
Another distinctive factor between meteoroids and asteroids is their location: meteoroids are dispersed throughout the solar system, while most asteroids can be found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Asteroids are the remains of debris of the formation of the planet in the early solar system, which means that scientists can learn a lot by studying their orbit, their rotation, their size, their shape and their composition.
Large asteroid impacts on earth are rare, although from the end of 2024 in early 2025, scientists closely monitored the 2024 asteroids, because his trajectory seemed to be a point of concern. However, at more in -depth observation, it was determined later that a collision would not occur.

Related
An asteroid heads towards the earth, but should we worry?
Spacer! Spacer! Bra … Wait, what? Oh okay.
Did you know? The mass extinction event 66 million years ago which would have suffered the dinosaurs of the earth was caused by an asteroid measuring up to 15,000 meters wide. This event – known as chicxulub impact – was resulted in a massive explosion and a heat wave, caused dust and debris to prevent sunlight from reaching the surface of the earth and triggered huge tsunamis and earthquakes, ultimately destroying 75% of all plant and animal species.
Now that you know the difference between meteors, weather, meteorites, comets and asteroids, go further by learning of the meaning of certain more complex spatial terms, such as cosmos, antiparticles, black holes, light years and absolute zero.